Keep our news free from ads and paywalls by making a donation to support our work!

Notes from Poland is run by a small editorial team and is published by an independent, non-profit foundation that is funded through donations from our readers. We cannot do what we do without your support.
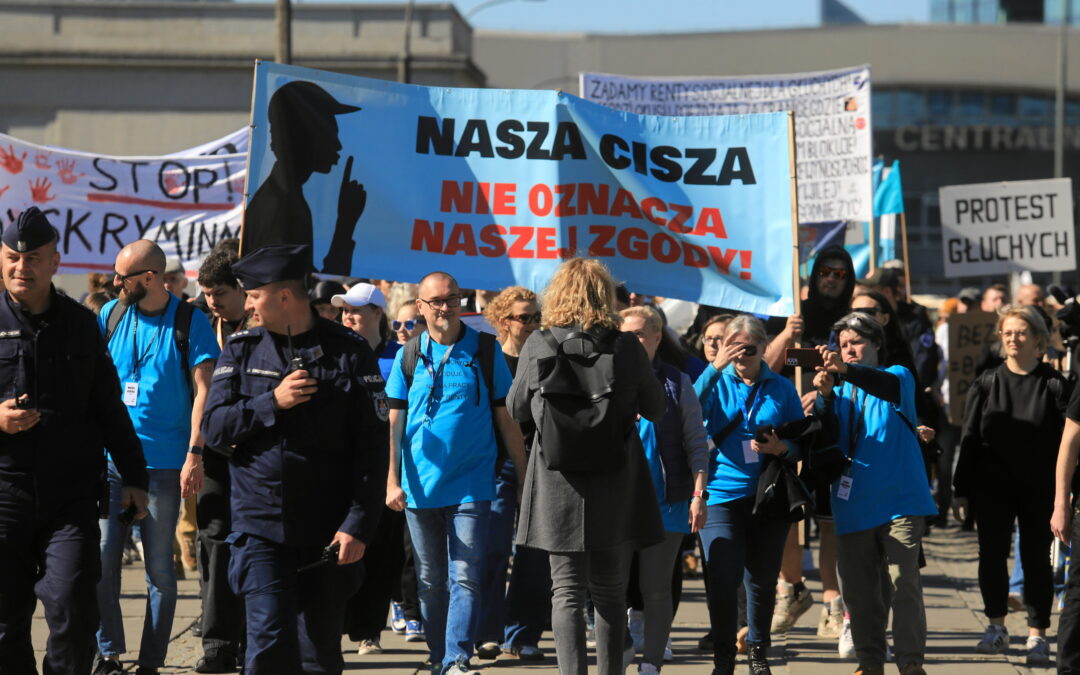
Several hundred people gathered in Warsaw on Friday to protest what they say is the Polish government’s neglect of the deaf community’s needs.
The protesters are demanding official recognition of sign language as a minority language, financial support for education, employment and daily life, improved access to interpreters, and workplace accessibility for deaf employees.
“Poland has been ignoring the needs of the Deaf community for years,” said deaf rights activist Agnieszka Szyc-Łuczywek on Facebook announcing the protest. “The state does not hear us, but we are there, and we will not be silenced,” she added.
Photos and video footage shared by media outlets and participants showed a large turnout at the demonstration. The protesters carried banners that read: “Deaf people have a voice, equal rights now”, “The state is robbing us because deaf people can’t shout,” and “stop discrimination”.
Some participants waved the blue and yellow flags of the Polish Deaf Association (PGZ). They also brought whistles, pots and drums, as the organisers encouraged the demonstrators to bring “anything to help us be heard”.
SETKI! SETKI LUDZI zbliżają się pod @MRPiPS_GOV__PL !@LukaszKrason @KKotyniewicz pic.twitter.com/iy2Stnthgo
— Małgorzata Szumowska (@MSzumowska) April 4, 2025
The protest organisers are calling for Polish law to recognise Polish sign language as an official minority language. That would allow it to be taught in schools and used in local administration in municipalities that meet certain conditions.
They are also demanding financial support for education, employment and daily life, as well as improved access to interpreters in hospitals and government offices.
Furthermore, they are urging the government to require employers to provide workplace accessibility for deaf employees.
According to Bartosz from Sosnowiec, a participant in the protest interviewed by the Gazeta Wyborcza daily, who has been deaf since birth, access to an interpreter in offices or medical facilities is essential for real access to public services for deaf people.
“A visit to the doctor? Without an interpreter, it’s often a lottery…Patients are called by name, and if someone doesn’t hear their name, they can wait for hours, not realising their turn has already passed,” he said.
The ministry of family, labour and social policy says that clinics, the police or the fire brigade are responsible for providing interpreters, not the government, reported the newspaper. In practice, deaf individuals often have to arrange and cover the costs of interpreters themselves.
Parents and other carers of disabled people protested in front of the Presidential Palace demanding the right to work part time without losing benefits.
They say it is difficult to survive on the 2,119 zl (€450) in nursing benefits they receive per month https://t.co/SORftQUQhR
— Notes from Poland 🇵🇱 (@notesfrompoland) November 22, 2022
According to the PGZ, there are currently around 50,000 people in Poland with severe to profound hearing impairment who use Polish sign language as their first language. Additionally, approximately 800,000 to 900,000 people have moderate hearing impairment.
This is the overhead kick by Poland's Marcin Oleksy that has just been named goal of the year by FIFA https://t.co/VLPP9IZw9wpic.twitter.com/JbPV7Ke0Qt
— Notes from Poland 🇵🇱 (@notesfrompoland) February 27, 2023

Notes from Poland is run by a small editorial team and published by an independent, non-profit foundation that is funded through donations from our readers. We cannot do what we do without your support.
Main image credit: Jacek Marczewski / Agencja Wyborcza.pl

Alicja Ptak is deputy editor-in-chief of Notes from Poland and a multimedia journalist. She has written for Clean Energy Wire and The Times, and she hosts her own podcast, The Warsaw Wire, on Poland’s economy and energy sector. She previously worked for Reuters.