Keep our news free from ads and paywalls by making a donation to support our work!

Notes from Poland is run by a small editorial team and is published by an independent, non-profit foundation that is funded through donations from our readers. We cannot do what we do without your support.
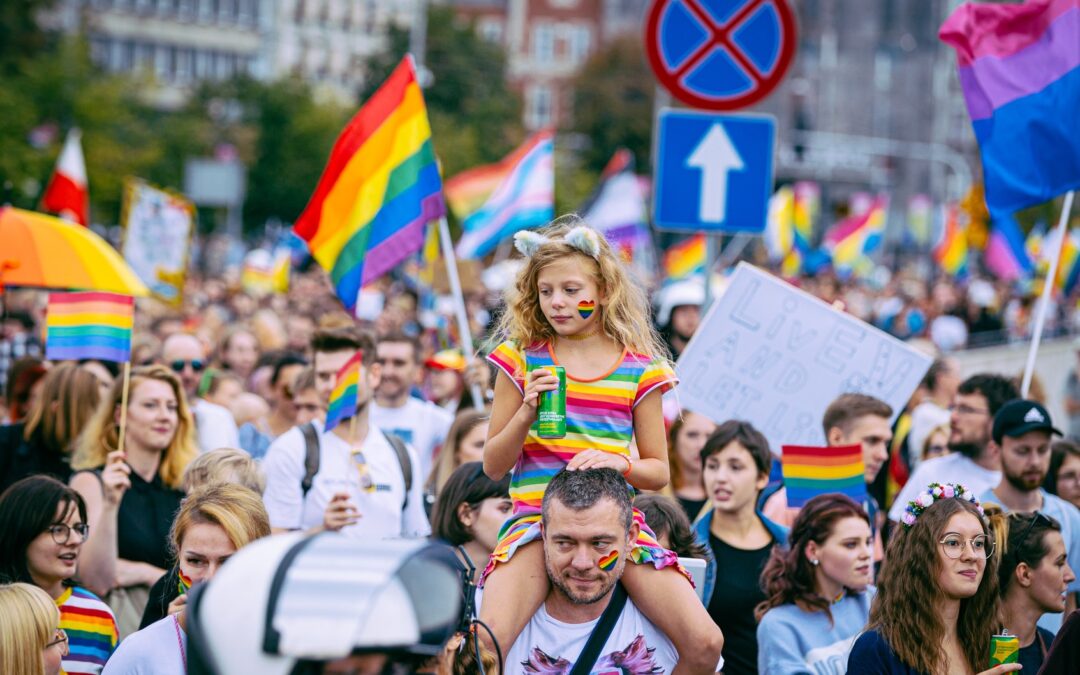
The last local authority in Poland to still have an anti-LGBT+ resolution in place has repealed the measure.
Just a few years ago, around one third of the country’s area was covered by such resolutions. But they have now all been withdrawn, in large part due to the threat of losing European funds.
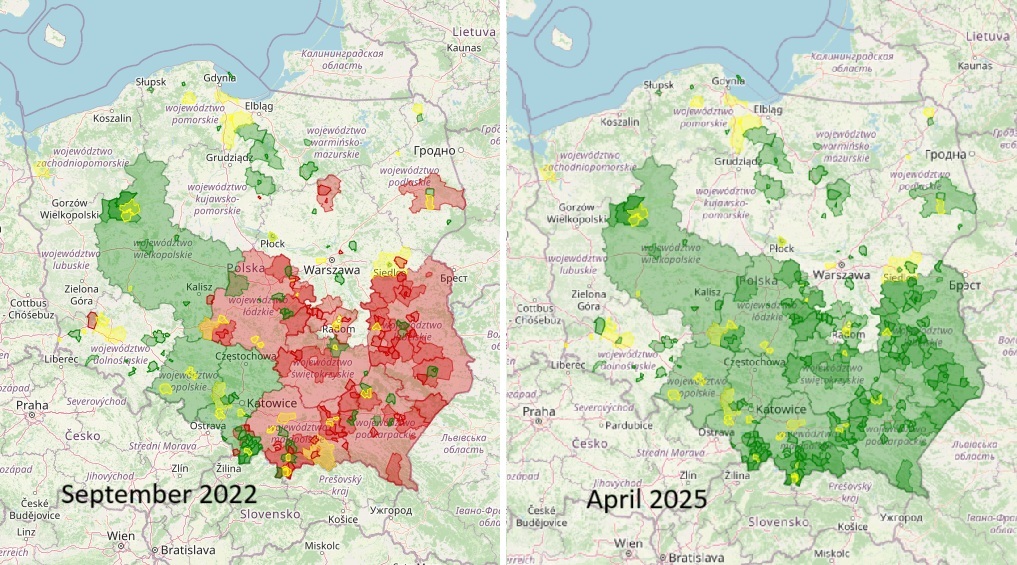
The “Atlas of Hate” showing local authorities in Poland that have active anti-LGBT resolutions (in red) and those that have rejected or withdrawn them (in green). Areas in yellow show where lobbying for such resolutions has taken place.
On Thursday this week, councillors in the county of Łańcut in southeast Poland held an extraordinary session with just one item on the agenda: whether to retain or repeal a so-called “charter of family rights” they had adopted in 2019. A majority of 13 out of the 18 council members voted to repeal it.
In a statement issued afterwards, the local authorities made clear that the decision had been made for financial reasons: due to the charter being in place, the county’s only medical centre is set to miss out on 750,000 zloty (€175,600) in EU funds.
“The [council] is of the view that the over 80,000-strong community of Łańcut county cannot be deprived of benefits resulting from participation in many programmes and grants,” they wrote. Their decision “is therefore aimed solely at preventing the exclusion of residents of Łańcut county”.
This is a final appeal for our emergency campaign to save Notes from Poland.
Next week, we may lose the major grant that sustains our work.
If you value the service we provide, please click below and make a donation to help it continue https://t.co/0gVkMlaA0W
— Notes from Poland 🇵🇱 (@notesfrompoland) April 22, 2025
In 2019 and 2020, over 100 local authorities around Poland adopted anti-LGBT+ resolutions. Some specifically declared their regions to be “free from LGBT ideology”, but most were the so-called “charters of family rights”, which do not mention the term “LGBT” specifically.
Instead, they express support for marriage as being exclusively between a man and a woman and pledge to “protect children from moral corruption” (language often used as part of anti-LGBT rhetoric).
After repealing its charter of family rights, Łańcut council maintained that it had “not contained any provisions discriminating against any group of people or individuals”. It hit out at the “aggressive” and “unfair” criticism the resolution had faced.
“It shows that the people or groups criticising the resolution in question probably did not even familiarise themselves with its entire contents,” wrote the local authority.
A local authority that was the first of many in Poland to adopt a resolution declaring itself “free from LGBT ideology” has now voted to withdraw the measure.
It did so under the threat of losing millions in EU funding over the issue https://t.co/kNP4jaSlhm
— Notes from Poland 🇵🇱 (@notesfrompoland) November 2, 2023
However, the LGBT rights activists behind the creation of an online “Atlas of Hate” that has mapped Poland’s anti-LGBT resolutions told broadcaster TVN of their “relief and satisfaction” at Łańcut’s decision.
“Thanks to the efforts of many people, groups and communities, over a hundred discriminatory anti-LGBT resolutions and family charters have disappeared from Poland,” said Paulina Pająk. “These resolutions were an extreme manifestation of systemic discrimination against LGBTQ+ people.”
“I am very glad that this stage is coming to an end,” added Jakub Gawron. “But that does not change the fact that these resolutions should not have been passed at all.”
Gawron also noted the important role the EU had played in bringing about the repeal of all the resolutions by prohibiting financing of projects involving local authorities that adopt discriminatory resolutions.
Uchwała SKPR powiatu łańcuckiego została uchylona!
Wszystkie strefy uchylone!
Nasz trud skończony!
Na bloga puściliśmy podsumowanie historii stref i Atlasu Nienawiści.
Uprzedzam – komunikat jest długi, bo dużo się działo przez te 6 lat 📷https://t.co/eJFSjpusIj pic.twitter.com/sTFn6Xf2Zi
— Atlas Nienawiści | Atlas of Hate ✨🦋| 🇺🇦🏳️🌈 (@AtlasNienawisci) April 24, 2025
In July 2021, the European Commission launched legal proceedings against Poland due to its anti-LGBT resolutions, which it argued “may violate EU law regarding non-discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation”.
Soon after, Brussels “put on hold” funding for Polish regions that had passed such resolutions, who were informed that “declaring LGBTIQ-free/unwelcome territories…constitutes an action that is against the values set out in the Treaty on European Union”.
The EEA and Norway Grants programme, which is separate from the EU and provides funds to Polish local authorities, also announced that it would not finance projects run by places that have passed anti-LGBT+ resolutions.
Poland has been ranked as the worst country in the EU for LGBT+ people for the fifth year in a row https://t.co/5ciljeroir
— Notes from Poland 🇵🇱 (@notesfrompoland) May 15, 2024
Most of the resolutions were passed with the support of the national-conservative Law and Justice (PiS) party, which led Poland’s national government at the time.
During PiS’s time in power, it led a vociferous campaign against what it called “LGBT ideology” and “gender ideology”. As a result, Poland slid to be ranked as the worst country in the EU for LGBT+ people.
In December 2023, a new, more liberal coalition came to power, promising to improve LGBT+ rights. However, it has so far failed to introduce planned new laws on same-sex civil partnerships and expanding hate-speech protection to LGBT+ people due to both internal divisions and opposition from the PiS-aligned president.
President Duda has not signed into law a government bill criminalising anti-LGBT+ hate speech.
Instead, he has sent it to the constitutional court for consideration, saying he has concerns it violates the right to free speech enshrined in the constitution https://t.co/jLHQvlCtup
— Notes from Poland 🇵🇱 (@notesfrompoland) April 17, 2025

Notes from Poland is run by a small editorial team and published by an independent, non-profit foundation that is funded through donations from our readers. We cannot do what we do without your support.
Main image credit: Max Bashyrov/Flickr (under CC BY-NC 2.0)

Daniel Tilles is editor-in-chief of Notes from Poland. He has written on Polish affairs for a wide range of publications, including Foreign Policy, POLITICO Europe, EUobserver and Dziennik Gazeta Prawna.



















